http://composingprograms.com/pages/11-getting-started.html
http://composingprograms.com/pages/12-elements-of-programming.html
1.1 Expressions 表达式
1.1.1 Types of expressions
上来先定义什么是 expression:
An expression describes a computation and evaluates to a value
”一个表达式描述的是一种计算,然后表达式最终会计算得出一个具体的值“
1.1.2 Call Expressions in Python
All expressions can use function call notation
“表达式里可以包含函数调用”
# Call expressions
max(2, 3)
min(1, -2, 3, -4, 5)
pow(100, 2)
pow(2, 100)1.1.3 Anatomy of a Call Expression 调用表达式剖析

Operators and operands are also expressions,So they evaluate to values.
就是说这个这俩玩意他都是 expressions,所以他俩能计算出来值
Evaluation procedure for call expressions:
1. Evaluate the operator and then the operand subexpressions
1. Apply the function that is the value of the operator
to the arguments that are the values of the operands
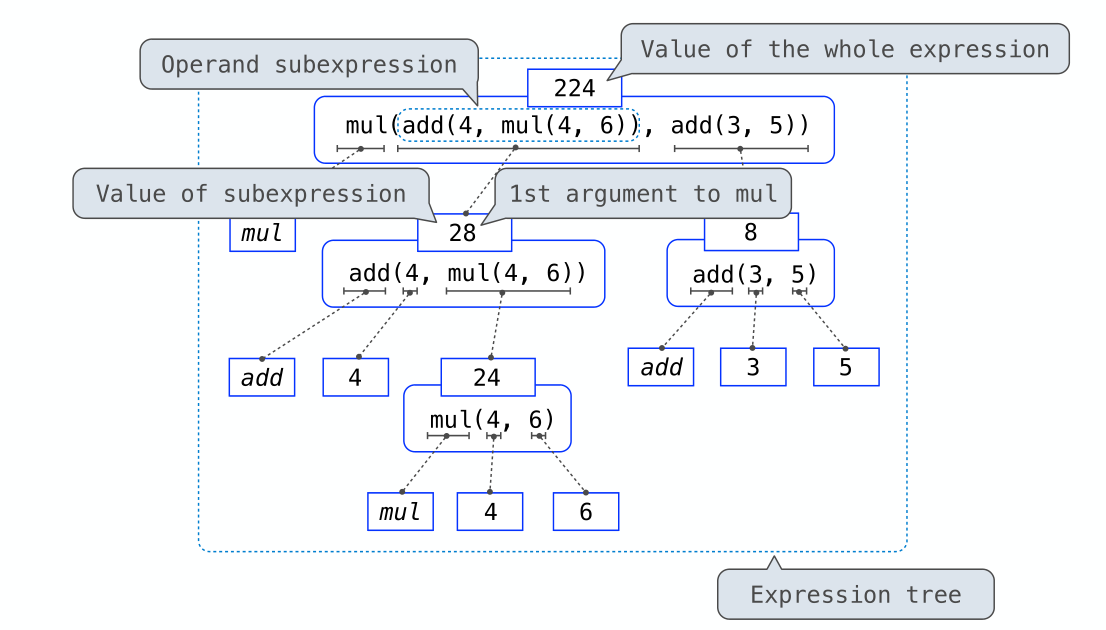
其实就是解释一下这是怎么回事,类似DFS
Names, Assignment, and User-Defined Functions
小技巧 ctrl+l 清屏 (似乎是苹果限定,俺的win不行)
先讲了赋值,函数名也能赋值
>>> max(1,2,3)
3
>>> f=max
>>> max
<built-in function max>
>>> f
<built-in function max>
>>> f(1,2,3)
3
>>> max = 7
>>> f(1,2,3)
3
>>> f(1,2,max)
7
>>> max(1,2,3)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'int' object is not callable
>>> max = f
>>> max(1,2,3)
3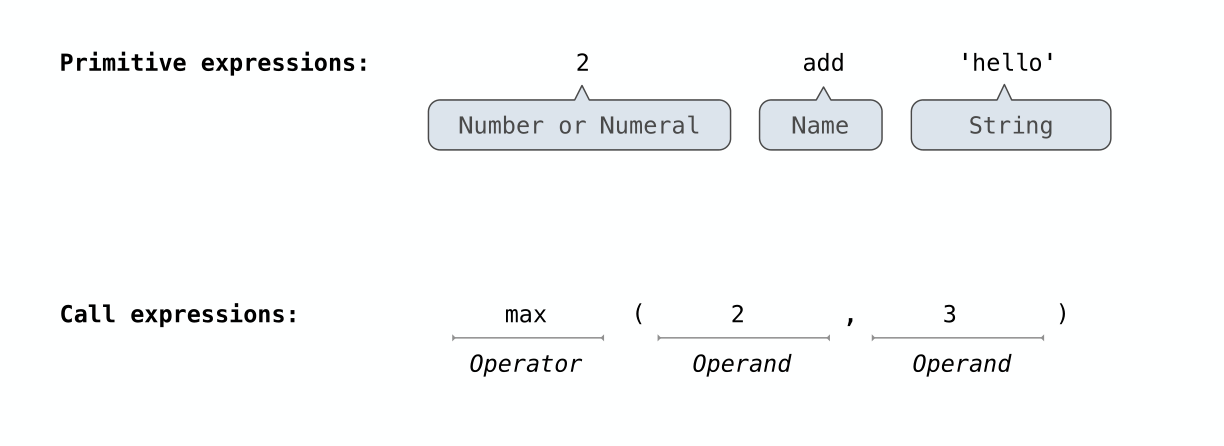
注意这里分出来了:Primitive exprsssions 和 Call expressions
Discussion Question 1
What is the value of the final expression in this sequence?
>>> f = min # f:min
>>> f = max # f:max
>>> g, h = min, max # g:min, h:max
>>> max = g # max:g:min 但是 f 和 h 没变 : f:max g:min h:max max:min
>>> max(f(2, g(h(1, 5), 3)), 4)详细的解析如下:
>>> f=min
>>> f
<built-in function min>
>>> f = max
>>> f
<built-in function max>
>>> g,h = min,max
>>> g
<built-in function min>
>>> h
<built-in function max>
>>> max = g
>>> g
<built-in function min>
>>> max
<built-in function min>
>>> f
<built-in function max>
>>> g
<built-in function min>
>>> h
<built-in function max>
>>> max(f(2, g(h(1, 5), 3)), 4)
3
>>> h(1,5)
5
>>> g(h(1, 5), 3)
3
>>> f(2, g(h(1, 5), 3))
3
>>> max(f(2, g(h(1, 5), 3)), 4)
31.2 Environment Diagrams 环境图
照例给出定义:
Environment diagrams visualize the interpreter’s process.
环境图可视化了解释器的过程。
对应网址:
https://pythontutor.com/composingprograms.html#mode=edit
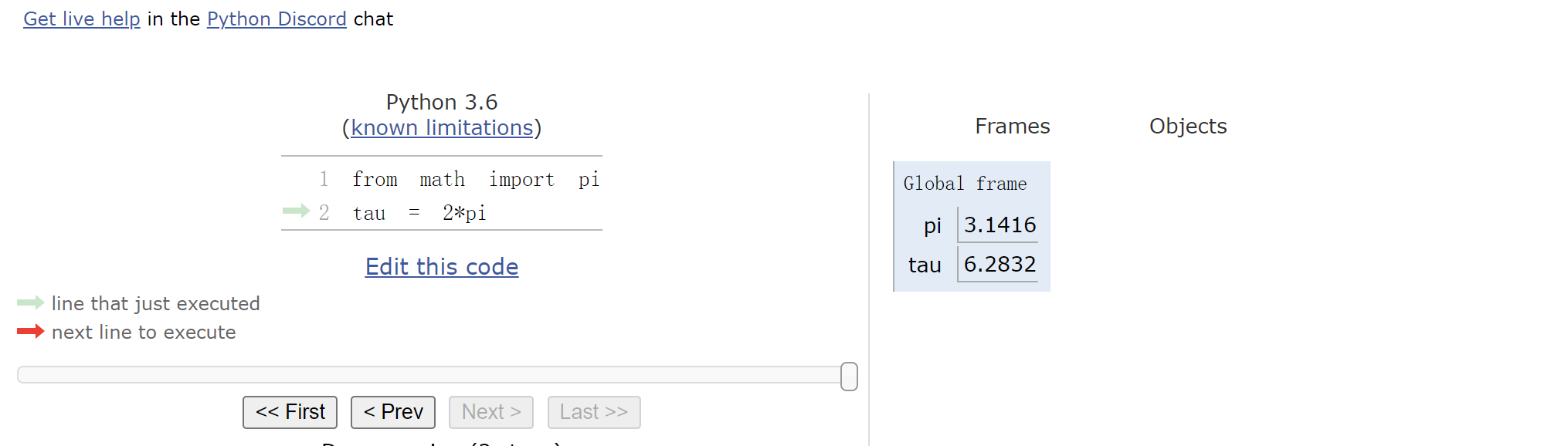
巴拉巴拉讲了这个玩意怎么用,然后去把上面的测试跑一下
Assignment Statements 赋值语句
讲赋值语句的执行规则
Execution rule for assignment statements:
1. Evaluate all expressions to the right of = from left to right.
2. Bind all names to the left of = to those resulting values in the current frame.
- 从左到右计算
=右边的表达式 - 在当前 frame 把计算结果绑定到
=左边的 name
1.3 Defining Functions 定义函数
Assignment is a simple means of abstraction: binds names to values
Function definition is a more powerful means of abstraction: binds names to expressions
区别于 Assignment ,函数:强!
函数的使用:
>>> def <name>(<formal parameters>):
return <return expression>注意途中定义了两个函数的细分:
- signature :函数的签名,即参数列表,指示函数采用的参数数
- body :函数体,应用函数时执行的计算
讲了def的执行过程:
Execution procedure for def statements:
1. Create a function with signature <name>(<formal parameters>)
2. Set the body of that function to be everything indented after the first line
3. Bind <name> to that function in the current frame尤其需要注意的是第三点,name 会 bind to function ,而且是在当前的 frame 下
Calling User-Defined Functions
用户定义的函数的执行过程:
Procedure for calling/applying user-defined functions (version 1):
1. Add a local frame, forming a new environment
2. Bind the function's formal parameters to its arguments in that frame
3. Execute the body of the function in that new environment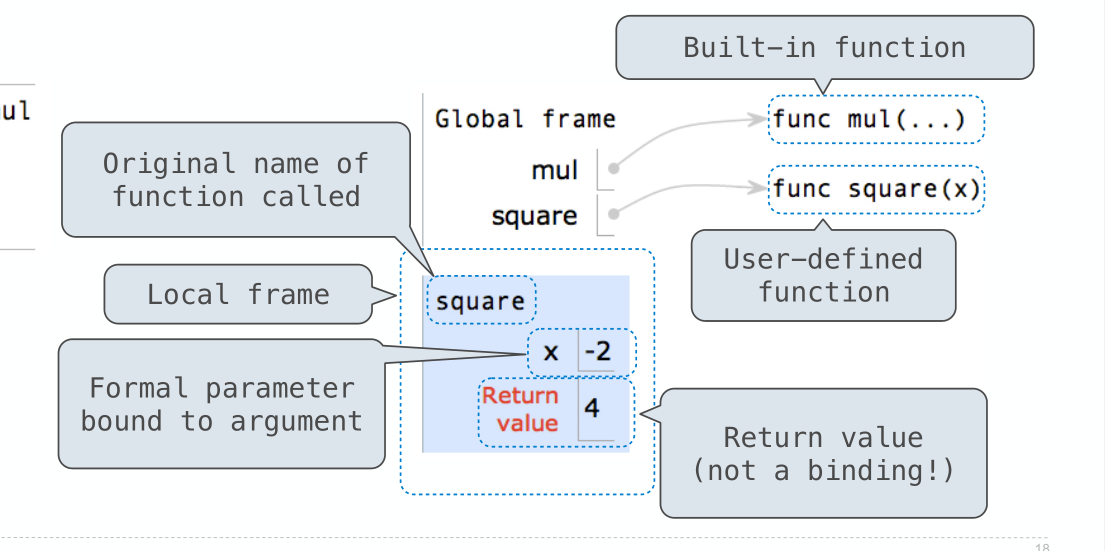
这个也非常有意思
- 当 calling 的时候,会 add a loacl frame,forming a new environment ,注意一个 add ,一个 forming
- 这时候会把 formal parameters 也就是经常说的形参绑定到 its
arguments(这个词又是啥) - 在新环境下执行
- 注意 是 return value ,而不是 binding
A function’s signature has all the information needed to create a local frame
这句话我不懂,能不能推定说是 local frame 只要有 formal parameters 就可以了,#todo
Looking Up Names In Environments
Every expression is evaluated in the context of an environment.
每个表达式都在环境的上下文中进行计算。
So far, the current environment is either:
- The global frame alone, or
- A local frame, followed by the global frame.
以及强调!!!:
An environment is a sequence of frames.
环境是一系列的 frame
A name evaluates to the value bound to that name in the earliest frame of the current environment in which that name is found.
名称的计算结果为在找到该名称的当前环境的最早帧中绑定到该名称的值。