10.1 Dynamic Method Selection Puzzle (Online Only)
10.1.1 A Typing Puzzle
上来先整一道题做做:
Suppose we have two classes: 有两个类
- Dog: Implements bark() method.
Dog实现了bark() - ShowDog: Extends Dog, overrides bark method.
ShowDog继承了Dog,override 了bark()
Summarizing is-a relationships, we have:
- Every ShowDog is-a Dog
- Every Dog is-an Object.
- All types in Java are a subtype of Object.
For each assignment, decide if it causes a compile error.
For each call to bark, decide whether:
- Dog.bark() is called,
- ShowDog.bark() is called, or
- A syntax error results.
The rules:
- Compiler allows memory box to hold any subtype.
- Compiler allows calls based on static type.
- Overridden non-static methods are selected at run time based on dynamic type. 在运行时根据动态类型选择被覆盖的非静态方法。
- Everything else is based on static type, including overloaded methods. Note: No overloaded methods for problem at left.
Object o2 = new ShowDog("M","C",25,512.2)
//is ShowDg is a Object?yes allowed
ShowDog sdx = ((ShowDog) o2);
// o2 的 static type 是 Object ,((ShowDog) o2)的 static type 是ShowDog allowed
sdx.bark();
//showdog 有 bark 方法么?有,调用 showdog.bark
Dog dx = ((Dog)o2);
//尝试把 static type:Object变 Dog allowed
Dx.bark();
// 注意 此时的dx的 dynamic type 是 showdog,调用 showdog.bark
((Dog)o2).bark();
// o2:static:Object , (Dog):Dog ,dog有bark?有。但是还是一样,o2 的 dynamic type是showdog
Object o3 = (Dog) o2;
// o2 是Object,allowed
o3.bark();
// o3:static:Object 没有 bark ,编译失败注意 Casting 这玩意 does not have any lasting effcet,只针对此表达式进行一个强制类型转换,不会对 static type 做改变,仅仅是为了类型检查而视为一个xx类
还有就是编译器仅仅通过静态类型来判断
10.1.2 Static Methods, Variables, and Inheritance
我们提出两个问题:
- What if a subclass has variables with the same name as a superclass? 若子类有与超类同名的变量怎么办
- What if subclass has a static method with the same signature as a superclass method?若子类具有与超类方法具有相同的静态签名咋办
- For static methods, we do not use the term overriding for this. 覆盖 Overriding 仅仅适用于非静态方法
但是不讲嘿嘿嘿
10.2 Subtype Polymorphism 子类多态性
首先 Polymorphism 是什么 : “providing a single interface to entities of different types”为不同类型的实体提供一个单一的接口
Subtype Polymorphism 就是调用那个方法的区别取决于对象的类型
E:
Consider a variable deque of static type Deque:
- When you call deque.addFirst(), the actual behavior is based on the dynamic type.
- Java automatically selects the right behavior using what is sometimes called “dynamic method selection”.
也就是说我们对以一个 deque ,不知道是 linked 还是 基于数组的,都会调用 deque.addFirst() ,到时候会进行一个 dynamic methond selection
def print_larger(x, y, compare, stringify): # 顺带一提 这里会被叫做 callback
if compare(x, y):
return stringify(x)
return stringify(y)def print_larger(x, y):
if x.largerThan(y):
return x.str()
return y.str()上段代码: Explicit HoF Approach
下段代码: Subtype Polymorphism Approach 这里是类做出了选择
10.3 DIY Comparison
教你写 max( ) 方法
10.3.1 how many compilation errors are there in the code shown?
public static Object max(Object[] items) {
int maxDex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < items.length; i += 1) {
if (items[i] > items[maxDex]) {
maxDex = i; }}
return items[maxDex];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog[] dogs = {new Dog("Elyse", 3), new Dog("Sture", 9),
new Dog("Benjamin", 15)};
Dog maxDog = (Dog) max(dogs);
maxDog.bark();
}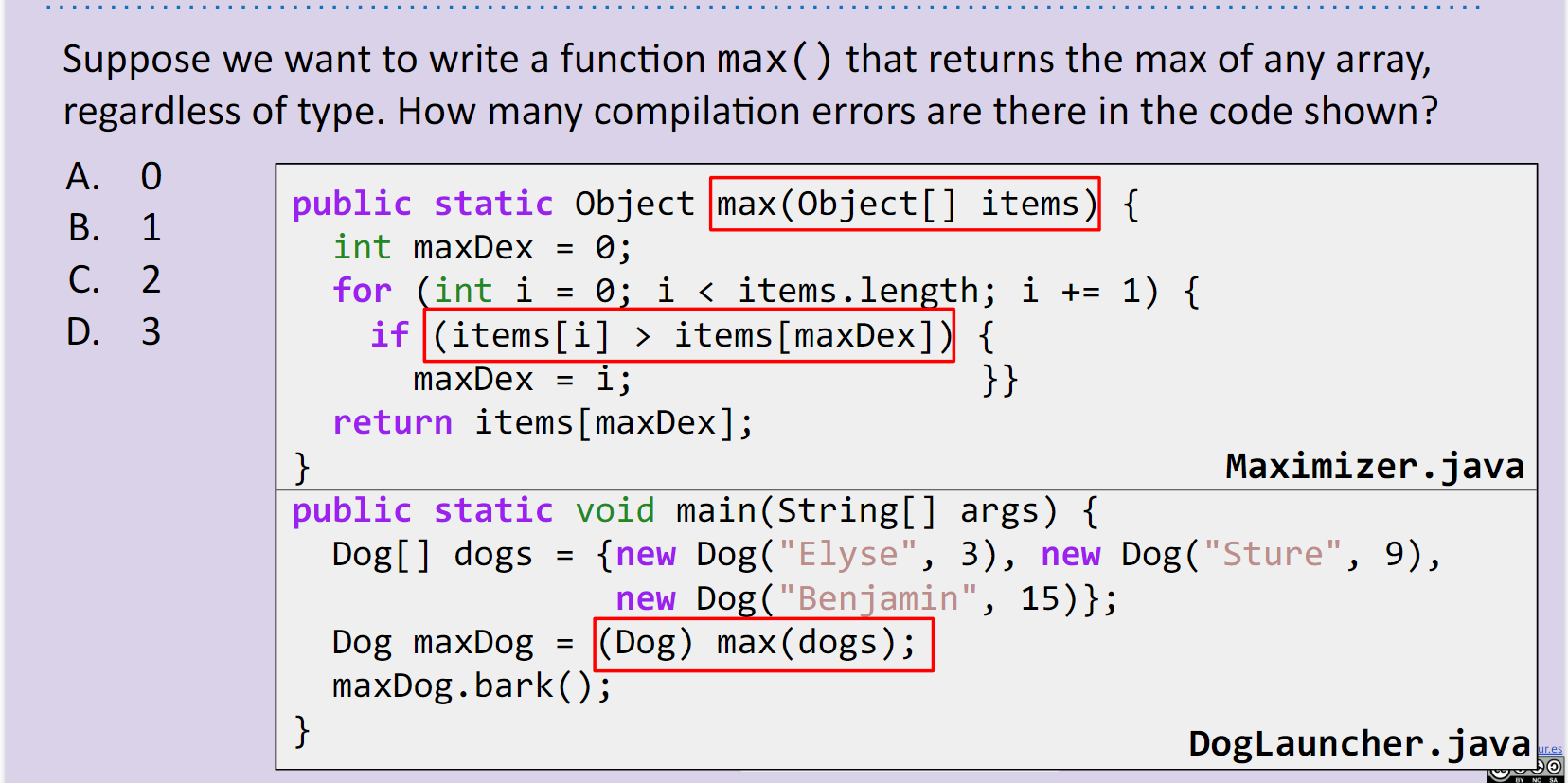
明显是B , > 的使用
当然可以特意给dog类去写一个 maxDog 方法,但是不优雅
10.3.2 Solution : interface inheritance
然而 java 是不支持运算符重载的,所以我们用 ”接口继承 interface inheritance“
interface inheritance says what a class can do, in this case compare.
如何做呢:
Create an interface that guarantees a comparison method.
- Have Dog implement this interface.
- Write Maximizer class in terms of this interface.
public static OurComparable max(OurComparable[] items) { ...具体实现:
public interface OurComparable {
int compareTo(Object obj);
}public class Dog implements OurComparable {
public int compareTo(Object obj) {
/** Warning, cast can cause runtime error! */
Dog uddaDog = (Dog) obj;
return this.size - uddaDog.size;
} ...public class Maximizer {
public static OurComparable max(OurComparable[] a) {
...
}我们使得 Dog are comparable ,而不是写了一个 max()
Dog[] dogs = new Dog[]{d1, d2, d3};
Dog largest = (Dog) Maximizer.max(dogs);10.3.3 Comparable
使用 java 内置的 interface comparable
public class Dog implements Comparable<Dog> {
@Override
public int compareTo(Dog uddaDog) {
//assume nobody is messing up and giving us
//something that isn't a dog.
return size - uddaDog.size;
}public class Maximizer {
public static Comparable max(Comparable[] items) {10.3.4 Comparators
def print_larger(T x, T y, comparator<T> c):
if c.compare(x, y):
return x.str()
return y.str()